

From Obergefell to Skrmetti: A Decade of Escalating Anti-Transgender Attacks
Over the past 10 years, LGBTQ community members and allies have seen major strides and significant setbacks in the fight for their rights. Though some legal protections have been established at the federal level, the uphill battle has never ceased. Legal attacks on LGBTQ individuals—particularly trans youth— are still pervade the country, threatening gender-affirming medical care, as well as individuals’ abilities to live their lives as their authentic selves. As this fight for bodily autonomy and gender expression continues, learn more about the legal battles that have helped LGBTQ rights over the past decade, and how the ACLU has helped to defend them.
10 Years of LGBTQ Legal Battles and the ACLU’s Defense
2015
June 26
The Supreme Court rules in the landmark case Obergefell v. Hodges that excluding same-sex couples from civil marriage is unconstitutional. This historic ruling marks a major step forward for LGBTQ equality in the United States, securing legal protections that families have built their lives around. But the ruling sparks backlash from anti-equality activists who begin testing new avenues to block legal protections for LGBTQ people.

November
A ballot campaign in Houston, Texas becomes the testing ground for a new kind of anti-LGBTQ messaging. Voters are presented a chance to support or reject Houston’s Equal Rights Ordinance (HERO), which would have enshrined local civil rights protections for veterans, people of color, disabled people, LGBTQ people and more. Anti-equality actors spread dangerous misinformation, stoking fear about transgender people using public restrooms, and ultimately succeed in defeating the measure at the ballot box.
2016
March
Anti-transgender bathroom bans gain steam as North Carolina politicians convene an emergency legislative session to repeal a Charlotte ordinance that would have protected LGBT people from discrimination in housing and public accommodations. The bill, HB2, also institutes a statewide ban on transgender people using restrooms in public buildings, including secondary schools, university, courthouses, libraries and public hospitals. A robust campaign to overturn the bathroom ban soon gained traction. Businesses left North Carolina, sporting events moved, and the law was challenged in court by the ACLU and Lambda Legal and a separate challenge was filed by the Department of Justice. Ultimately, North Carolina Governor Pat McCrory lost his re-election bid after staking much of his campaign on his support for the anti-transgender measure.
2017
November
Following resounding outcry against North Carolina’s HB2, other political efforts to enact anti-transgender legislation fail. Across the country, ballot measures seeking to roll back protections for transgender people, or codify anti-transgender policies, are unsuccessful.
2018
November
Advocates in Massachusetts make history by winning the first statewide popular vote on transgender rights, upholding a nondiscrimination law at the ballot box.
2019
March
Congress introduces the Equality Act, a bill that would add specific protections for LGBT people into federal civil rights statutes. But anti-equality campaigners mount an aggressive campaign to stop the bill by claiming that the codification of civil rights protections for transgender people would threaten women and girls.

2020
February
The notoriously anti-transgender Alliance Defending Freedom (ADF) sues Connecticut over its transgender-inclusive athletics policy, driving new scrutiny of transgender youth in sports. This announcement foreshadows a wider assault, as ADF begins to flood statehouses across the nation with model legislation attempting to push transgender people out of public life, starting by banning transgender people from playing sports.
June 15
The Supreme Court delivers a historic victory for LGBTQ rights in Bostock v. Clayton County. In a 6-3 opinion authored by Justice Neil Gorsuch, the Court finds that three LGBTQ workers who were fired because of their identity–including ACLU client and transgender woman Aimee Stephens–were discriminated against on the basis of their sex, in violation of Title VII of the 1964 Civil Rights Act. The ruling begins to unlock progress for equality beyond the workplace. Anti-LGBTQ extremists decry this victory and vow to fight back, redoubling their attacks on transgender people.

2021
April
Arkansas becomes the first state to pass a law banning essential medical care for transgender youth. Republican Governor Asa Hutchinson vetoes the bill, citing the danger of government overreach into the private and vulnerable decisions of adolescents, their parents and their doctors, but the legislature swiftly overrides his veto.
The law is quickly challenged in federal court by the ACLU and the ACLU of Arkansas on behalf of four transgender youth and their families and two doctors who treat transgender adolescents with the banned medication.
July
A federal district court judge applies heightened scrutiny to the law and issues a preliminary injunction against its enforcement, finding it likely unconstitutional.
2022
February
Texas Gov. Greg Abbott directs the state’s family policing agency, the Texas Department of Family Protective Services (DFPS), to begin investigating parents with transgender teens—a directive the ACLU is still fighting in court today with Lambda Legal. Meanwhile, in the statehouse, Texas politicians introduce a record number of anti-LGBTQ bills.
April
Alabama becomes the first state in the country to pass a law threatening felony convictions for providers of gender-affirming medical care to transgender people under 19. The law is soon challenged by families and the Department of Justice and blocked by a federal district court judge applying heightened scrutiny.
June
In Dobbs v. Jackson Whole Women’s Health, the Supreme Court overturns Roe v. Wade and ends nearly fifty years of constitutional protection for abortion access. The ruling has a devastating effect on abortion access across the country as sweeping bans take effect. Within days, the opinion from Justice Samuel Alito is cited by multiple states in defense of their bans on gender-affirming medical care.

August
A unanimous panel of the Eighth Circuit Court of Appeals affirms the district court’s preliminary injunction in the ACLU’s challenge to Arkansas’s ban on medical care for transgender youth.
2023
January
After enacting dozens of laws targeting transgender youth in schools and athletics, states begin to join Arkansas and Alabama and swiftly pass bans on gender-affirming medical care. By the end of 2023, 21 states will have banned this health care for transgender people under 18, with four states imposing a felony charge on violations of their ban.
April
LGBTQ advocates and legal organizations, including the ACLU and its nationwide affiliate networks, file legal challenges against these bans in federal and state courts across the country. The ACLU and its affiliates alone file 12 lawsuits against these bans.
Three families with transgender youth and a health care provider sue Tennessee, challenging the state’s ban on essential medical care for transgender youth. Represented by the ACLU, Lambda Legal, the ACLU of Tennessee, and Akin Gump Strauss Hauer & Feld LLP, families argue that the ban violates the Equal Protection Clause and the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
June
In quick succession, bans in Indiana, Tennessee, Kentucky, Georgia, and Florida are blocked from enforcement by federal district court judges, all of whom apply heightened scrutiny and find the laws are likely unconstitutional. The judges are highly critical of evidence presented by the states and emphasize the likelihood of severe harm to transgender youth in these states if the laws are allowed to be enforced while the trials proceed. In Arkansas, a federal judge permanently blocks Arkansas’ ban after a two-week trial.
July
The Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals allows Tennessee’s ban to take effect after Tennessee files for emergency relief. . The ruling has a “domino effect” in other appellate courts, and many of the laws blocked by district court judges are allowed to go into effect either immediately or on their effective date. The estimated number of transgender youth who live in a state with a ban is over 100,000.
November
Plaintiffs in the challenges to Tennessee and Kentucky’s bans ask the Supreme Court to review the Sixth Circuit’s opinion. The families challenging both bans are represented by leading LGBTQ rights organizations, including the National Center for Lesbian Rights, Lambda Legal, and the ACLU and both its Kentucky and Tennessee affiliates. The Department of Justice, which also challenged Tennessee’s ban, also requested the Supreme Court to review the Sixth Circuit’s decision.
2024
June
The Supreme Court announces that it will hear arguments in the challenge to Tennessee’s ban on medical care for transgender adolescents.
September
Dozens of amicus briefs are filed in support of plaintiffs, including from 20 state attorneys general, 164 members of Congress, constitutional law scholars, experts in sex discrimination, civil rights law scholars, historians, leading medical organizations, medical researchers, bioethicists, family physicians, parents of transgender youth, and transgender people who began gender-affirming medical care as minors and are now thriving adults.
December 4
The Supreme Court hears oral arguments in U.S. v. Skrmetti. Tennessee takes aim at foundational equal protection principles and urges the court to expand the Dobbs decision to limit constitutional protections for everyone.
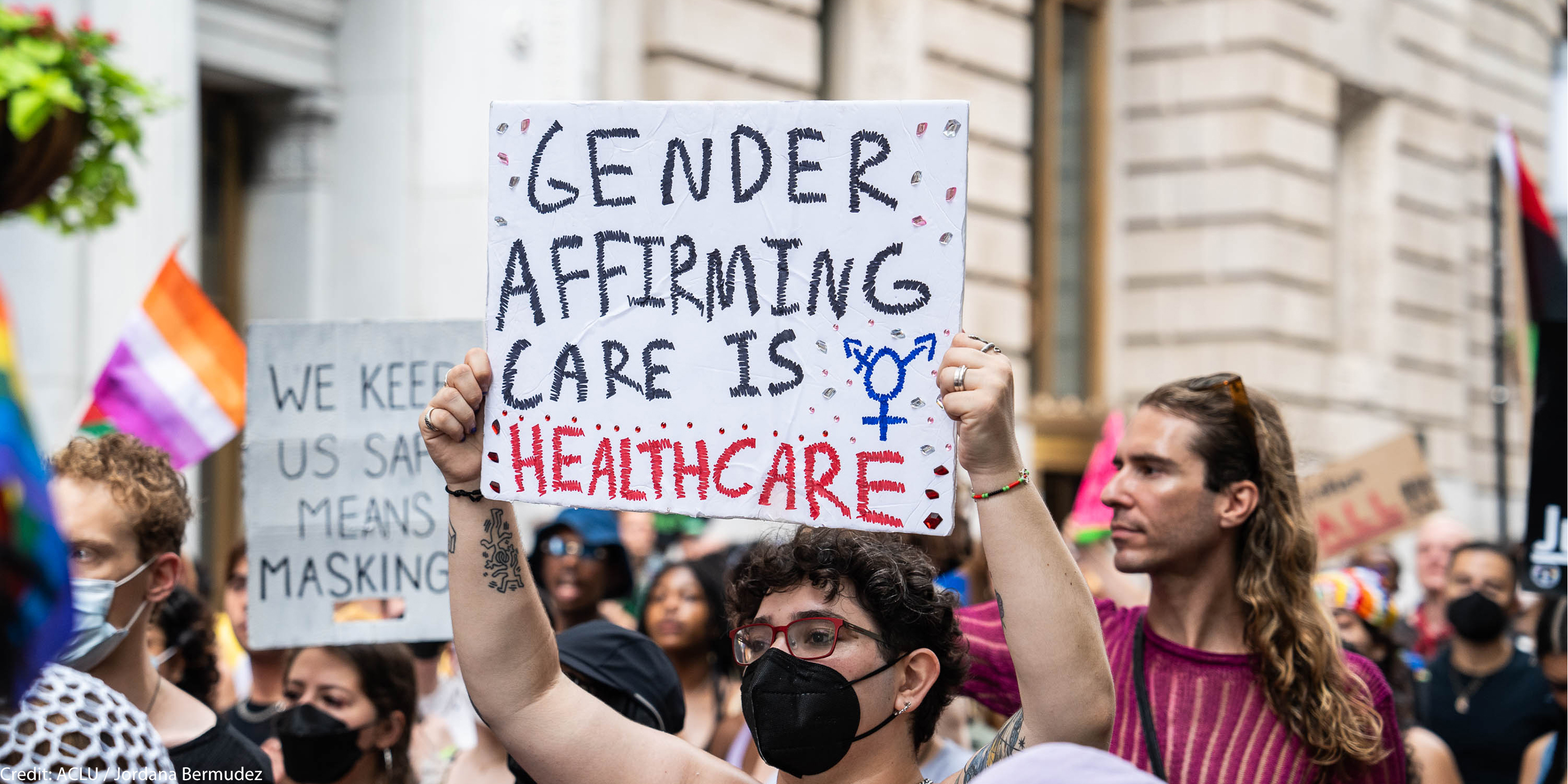
2025
January
The new Trump administration unleashes a flurry of anti-transgender executive orders, targeting transgender people’s access to health care, accurate passports and identification, and more.
February
The Trump administration tells the Supreme Court that it is reversing its position and siding with Tennessee in Skrmetti, but urging the court to rule before the end of the term.
In PFLAG v. Trump, the ACLU and Lambda Legal challenge the Trump administration’s executive order threatening to withhold federal funding from providers of gender-affirming medical care to any trans person under 19. A federal district court preliminarily blocks enforcement of the order.